The state of the art in indoor self location using Arduino sensor projects
Introduction
One of the most challenging things about self-location is that it does not work well indoors. This is because there are significant obstacles and reflections that can make a person’s location hard to pinpoint, even if they are near one of the sensors.
What is the state of the art in indoor self location using Arduino sensor projects?
Arduino sensor projects are becoming increasingly popular for indoor self-location. While there are many different approaches to this problem, the most common one is using a combination of sensors to detect changes in the environment and then use that data to estimate the location of the device. This article will explore some of the most recent advances in this field and discuss what the future may hold for indoor self-location using Arduino sensor projects.
Tracking methods for individual objects
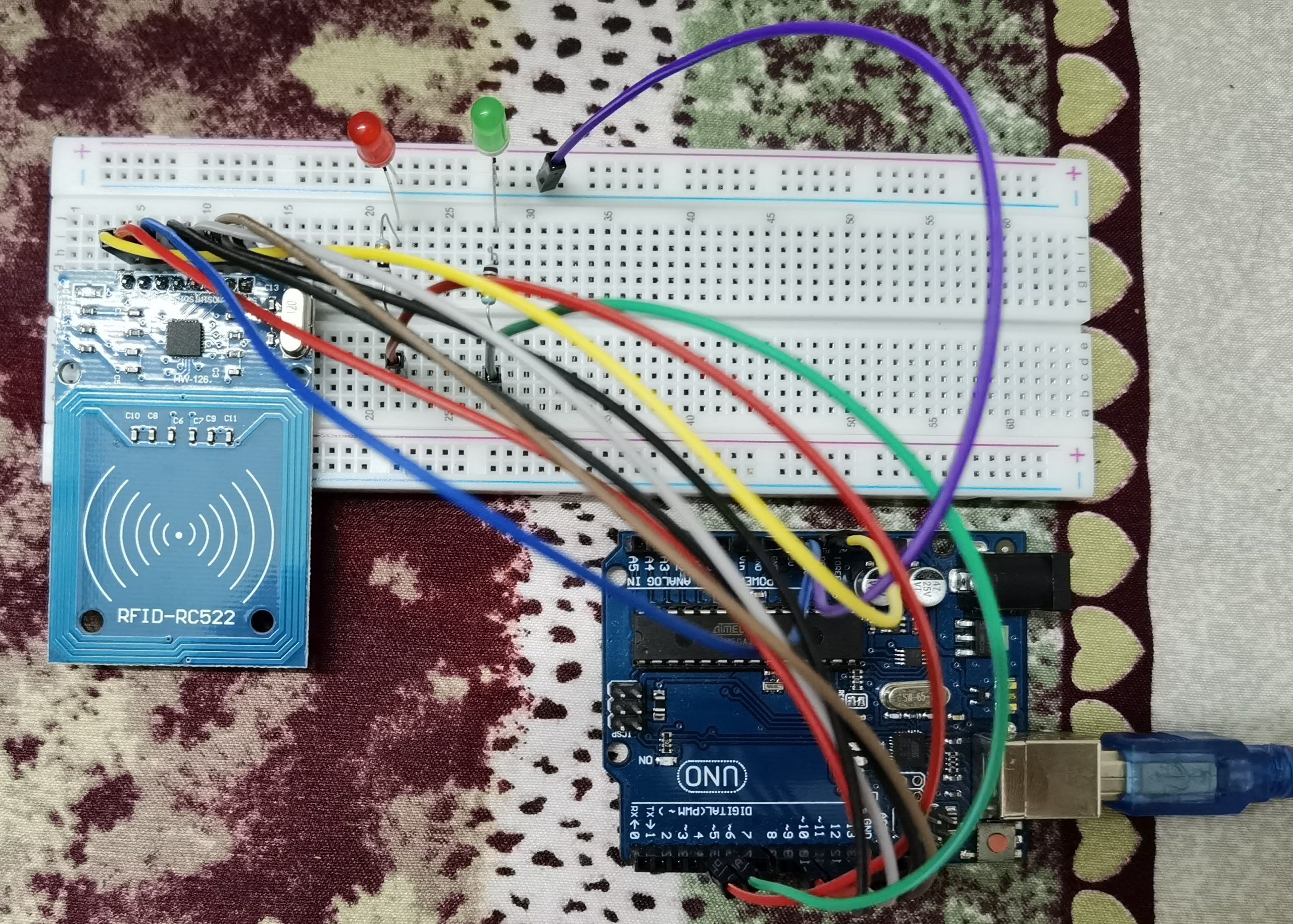
There are many ways to track the location of an object indoors using Arduino sensors. One common method is to use a radio frequency identification (RFID) system. RFID tags can be attached to objects and then read by an RFID reader. The reader can be connected to an Arduino board, which can then track the location of the tag.
Another common tracking method is to use an infrared (IR) sensor. IR sensors can be used to detect the presence of an object in a particular area. By placing several IR sensors around a room, it is possible to track the movement of an object from one sensor to another.
There are many ways to track the location of an object indoors using Arduino sensor projects. The most common method is to use GPS, but there are also other methods that can be used, such as RFID or sonar. GPS is the most accurate method, but it can be expensive and requires a clear view of the sky. RFID is less accurate but much cheaper, and sonar is somewhere in between.
Tracking motion for a group of people
There are many different types of indoor self-location systems that use Arduino sensor projects. Some of these systems use GPS tracking, while others use a combination of motion sensors and WiFi triangulation. The state of the art in indoor self-location systems is constantly evolving, as new technologies are developed and new applications are found for existing technologies.
There are many different types of indoor self-location systems that use various sensors and technologies. Some of the most popular systems make use of Arduino sensor projects. These systems can be used to track the movement of a group of people, or even an individual. The most popular indoor self-location system is the GPS system. However, there are other systems that use various sensors and technologies.
Motion based navigation system
There are many indoor self-location systems that use Arduino sensors to detect movement and navigate accordingly. Some of these systems use GPS tracking, while others use dead reckoning (a process of estimating one’s current position based on a previously determined position, direction, and speed). Some systems use a combination of both GPS and dead reckoning.
The accuracy of these indoor self-location systems can vary depending on the type and number of sensors used. Generally speaking, systems that use more sensors tend to be more accurate than those that use fewer sensors. Additionally, systems that use GPS tracking tend to be more accurate than those that rely solely on dead reckoning.
Conclusion
The state of the art in indoor self location using Arduino sensor projects is constantly evolving. While there are a variety of different approaches that can be taken, the most accurate results are typically achieved by using a combination of sensors. This allows for more accurate triangulation and ultimately a more precise location. As technology continues to improve, it is likely that the accuracy of these systems will only get better, making them an increasingly valuable tool for both personal and commercial use cases.
